Parallel Progressive Radiosity with Parallel Visibility Computations Article
Wolfgang Stürzlinger, Christoph Wild
Abstract:
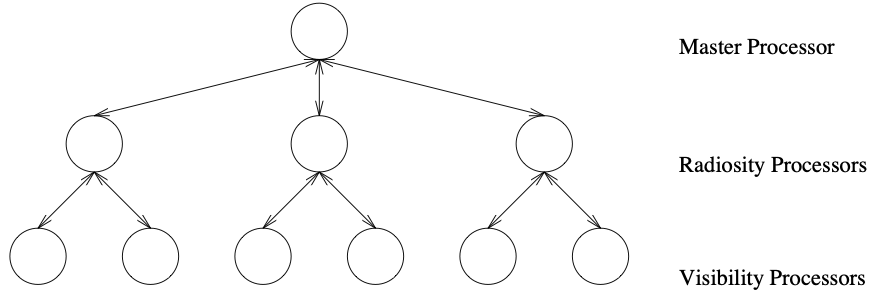
The radiosity method models the interaction of light between diffuse reflecting surfaces, thereby accurately predicting global illumination effects. Due to the high computational effort to calculate the transfer of light between surfaces and the memory requirements for the scene description, a distributed, parallelized version of the algorithm is needed for scenes consisting of thousands of surfaces. We present a distributed, parallel radiosity algorithm, which can subdivide the surfaces adaptively. Additionally we present a scheme for parallel visibility calculations. Adaptive load redistribution is also discussed.
Date of publication:
Feb - 1994
Footnote:
Conference proceedings later republished as journal volume by publisher