Shift-Sliding and Depth-Pop for 3D Positioning Inproceedings
Junwei Sun, Wolfgang Stuerzlinger, Dmitri Shuralyov
Abstract:
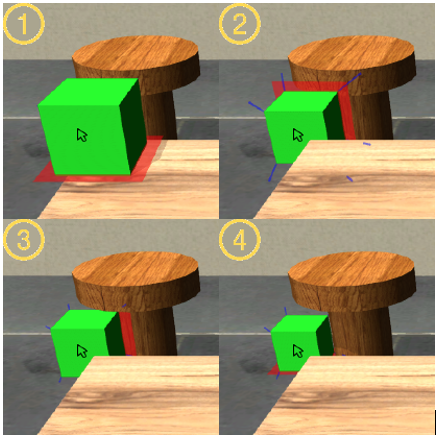
Moving objects is an important task in 3D user interfaces. We describe two new techniques for 3D positioning, designed for a mouse, but usable with other input devices. The techniques enable rapid, yet easy-to-use positioning of objects in 3D scenes. With sliding, the object follows the cursor and moves on the surfaces of the scene. Our techniques enable precise positioning of constrained objects. Sliding assumes that by default objects stay in contact with the scene's front surfaces, are always at least partially visible, and do not interpenetrate other objects. With our new Shift-Sliding method the user can override these default assumptions and lift objects into the air or make them collide with other objects. Shift-Sliding uses the local coordinate system of the surface that the object was last in contact with, which is a new form of context-dependent manipulation. We also present Depth-Pop, which maps mouse wheel actions to all object positions along the mouse ray, where the object meets the default assumptions for sliding. For efficiency, both methods use frame buffer techniques. Two user studies show that the new techniques significantly speed up common 3D positioning tasks.